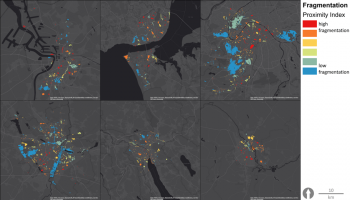
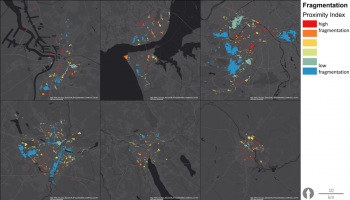
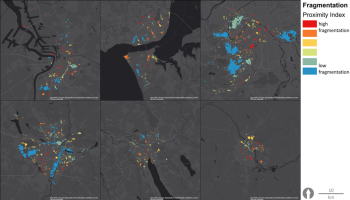
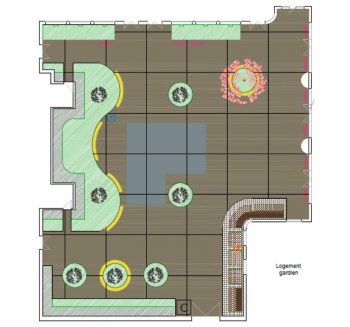
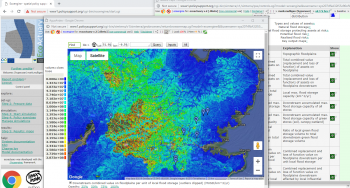
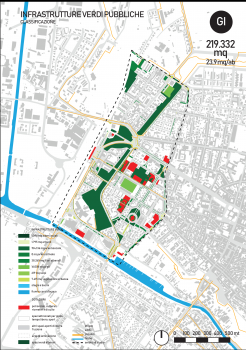
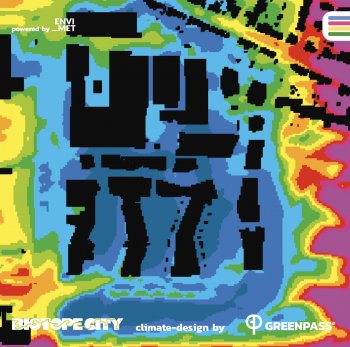
Urban hybrid dunes in Barcelona
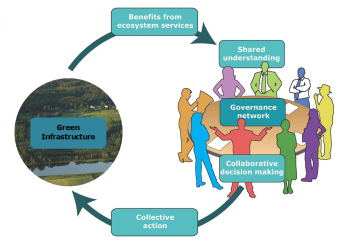
Constructing and maintaining semi-fixed dunes on heavily used urban beaches to optimize the flows of ecosystem services, through collaboration with administrations and stakeholders. Dunes play a central role in coastal defence and protection against sea level rise linked to climatic change. Stakeholder mapping and social research will be used to learn how to shape social attitudes to make the year-round intensive recreational use of beaches compatible with the protection of the dunes.