Application of Eco:Actuary in the Thames catchment, UK: A series of tools to operationalise strategic planning and investment for Natural Flood Management. H2020 NAIAD Project.
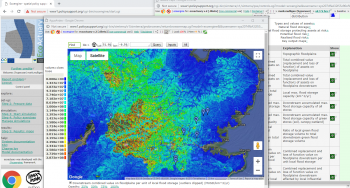
Using the widely used Policy Support System tools at www.policysupport.org as a basis, we built an insurance industry-relevant policy support system called Eco:Actuary. The objective of this project is to to co-develop and test the Eco:Actuary with NAIAD project partners & stakeholders in the fluvial non-tidal Thames as a DEMO catchment in the NAIAD project.
EcoActuary is an open-access catastrophe model capable of assessing the impact of NbS on local and downstream assets at risk of flood. It simulates a minimum of 1200 spatial...