Marketplace
- Document
Mapping of forest roads to support touristic activities
OG SURF has mapped the existing roads in its test areas using GNSS receivers and classified them based on their functionality, and identifying any maintenance issues, a prerequisite for identifying additional roads/trials to be opened in the forest.
UrbanByNature Programme in Brazil, the Caucasus, Korea and China
To make sure that the valuable processes and outputs of the Connecting Nature project can also go global and inspire local governments beyond Europe in the planning, implementation and upscaling of nature-based solutions, a knowledge exchange and capacity-building programme called UrbanByNature was
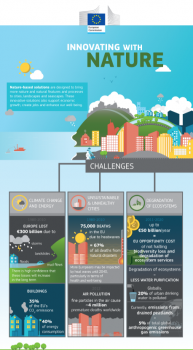
Innovating with Nature: Nature-based solutions
This infographic shows how nature-based solutions can play an important role in solving several of the challenges that our society is living nowadays, such as: Climate change and energy, Unsustainable and unhealthy cities or degradation of ecosystems.
GIZ ValuES - Method Profile: Scoping ecosystem services for impact assessment (WRI)
This manual for scoping ecosystem services is related to impact assessments. It enables the identification of key ecosystem services that could be impacted by or could constrain the successful implementation of projects at a point when they can still be modified. The complete manual covers six
ThinkNature Nature-Based Solutions Handbook
This Handbook has been developed in the framework of the ThinkNature project. Its main objective is to gather and promote state-of-the-art knowledge regarding Nature-Based Solutions (NbS), comprising a comprehensive guide to all relevant actors. To this end, each aspect of NbS is investigated, from
How Will Nature Restoration Help Fulfil EU Environmental Policy Objectives?
The EU Commission published its proposal for a new Nature Restoration Regulation in June 2022. In this context, IEEP and Ecologic Institute – as part of the Think Sustainable Europe network – published a series of thematic policy briefs to inform Members of the European Parliament and other
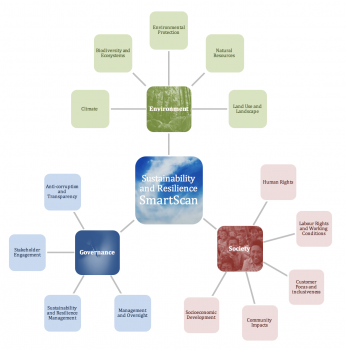
GIB SmartScan
Increase your infrastructure project’s attractiveness to investors in only a few steps. The GIB SmartScan allows you to assess your infrastructure projects based on its Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) issues and helps to efficiently flag risks and opportunities for improvements of your
Conexus key learning factsheet series - Supporting Nature-based Solutions via Nature-Based Thinking
In response to critiques of Nature-based Solutions (NbS), we propose a holistic and systemic approach: Nature-Based Thinking (NBT). NBT emphasizes the inspiration from nature to foster sustainable urban development and conceives nature to be intertwined with people. NBT will engage local actors,
Sprawl Monitor
Toolkit for monitoring urban sprawl and evaluating threats to sustainability.
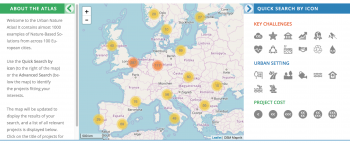
Urban Nature Atlas
The Urban Nature Atlas was developed in 2017 as an output of the Naturvation project (NATure-based URban innoVATION, a Horizon 2020 research project). The Atlas sought to collect evidence on nature-based solutions in order to provide a basis for the analysis of socio-economic and innovation
Taking real steps in virtual nature: a randomized blinded trial
Studies show that green exercise (i.e., physical activity in the presence of nature) can provide benefits of both physical exercise and nature exposure. The present study aimed to investigate the extent to which virtual green exercise may extend these benefits to people that are unable to engage in
CHILDREN’S URBAN NATURE LAB IN VUORES
In April, a children’s urban nature lab was organised in Vuores, inviting children from day care centres, preschools and primary schools to participate in the development of nature-based systems in Vuores. The children learned about the role of basins and wetlands in water purification, the plants
NetworkNature and NetZeroCities join forces to address interconnected challenges of climate and biodiversity in cities
Find out how Nature-based Solutions (NbS) can contribute to your transition to climate neutrality and biodiversity resilience by 2030. In the dynamic landscape of climate and biodiversityaction, cities play a crucial role. Collaboration and networking are essential for (re)integrating nature into
Europe’s Natural Treasures – an illustrated ecosystem services map
Europe is full of natural treasures that provide endless inspiration, excitement, and enjoyment as well as supporting much of our economy. These benefits we get from nature sometimes referred to as ecosystem services, that are provided by Europe's natural capital. This map provides a rich
Integrated Assessment and Valuation of Ecosystem Services: Guidelines and Experiences
As the ecosystem service concept has become more widely recognised, so the number of biophysical, socio-cultural and monetary methods available to assess ecosystem services has increased. There is relatively little guidance on how to select and combine these methods into hybrid approaches that
NetworkNature Annual Event Report 2023: Enabling transformation through and for Nature-based Solutions
The report summarises the key outcomes of the NetworkNature Annual Event 2023 “Enabling transformation through and for Nature-based Solutions”, which took place on 8th June 2023, at the Flagey Building in Brussels and brought together more than 150 participants to discuss the transformative nature
- Document
A Comprehensive Overview of Nature-Based Solutions
The term Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) comprises various approaches that address social and environmental challenges in a way that is beneficial to both biodiversity and human well-being. To establish a common understanding of the NBS concept among all stakeholders in the ENABLS project, this
Seedbed Intervention: Tallinn
The City of Tallinn’s seedbed intervention took place on the 10th September 2022 at Vormsi park’s green area in Lasnamäe district. There were guided walks organised in two languages - Estonian and Russian, in order to engage residents with different nationalities. Both walks were guided by two
Climate change in 12 pictures
This colourful and illustrative brochure was developed within the IUCN's initiative ADAPT: Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for resilient communities in Western Balkans. It represents a short guide through the climate change consequences showcasing possible solutions to climate change adaptation
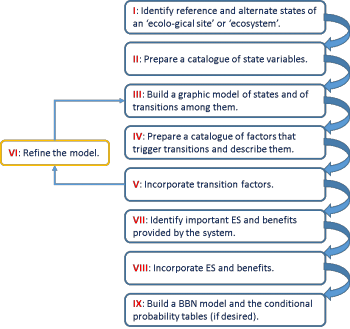
Method Factsheet - State and Transition Models
State-and-transition models (STMs) are conceptual models of ecosystem dynamics after disturbances based on alternate state theory (Kachergis et al. 2011). STMs combine the representation of alternate states and the factors that drive the transitions among states with tables of qualitative
- ‹ previous
- 34 of 45
- next ›