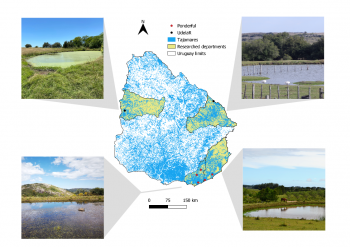
Despite their critical importance for biodiversity and significant potential as nature-based solutions for climate change mitigation and adaptation, ponds and pondscapes have traditionally been undervalued and overlooked.
The Horizon2020 PONDERFUL project brought together an international consortium to investigate the potential of these small habitats as nature-based solutions. This new knowledge, along with existing expertise from the PONDERFUL partners, has been brought together into a new technical handbook.
Ponds and Pondscapes: A technical guide to the use of ponds...