Area characterisation:
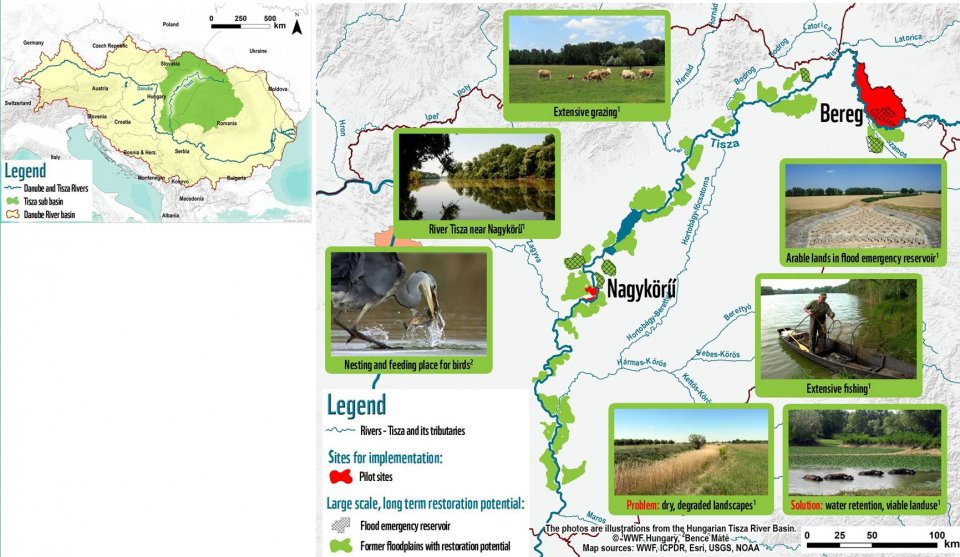
The Tisza basin is the largest sub-basin in the Danube River Basin. The Tisza was strongly regulated, floodplains were cut off from the river in the 19–20th centuries. Landscapes are dominated by intensive arable farming and draining the waters dries the landscapes.
Affected areas: Pilot Site A approx. 300 ha, Pilot Site B approx. 1,500 ha, Pilot Site C approx. 38,000 ha (27 municipalities, mostly belonging to the Vásárosnamény district by the river Tisza)
Objective:
Implementing floodplain farming systems in multiple sites along the Tisza River, thereby making land use more sustainable and in line with nature conservation efforts.
Actions:
- Planning and implementing a floodplain farming system in the floodway of river Tisza near Nagykörü based on water retention in former wetlands, and restoring habitats (Pilot Site A)
- A local farmer irrigation community will be established at another site, in the floodway fringe of the Tisza to create the infrastructure for providing water for farming and habitat restoration, reconnecting former floodplains to the river (Pilot Site B)
- A regular inundation regime within the Bereg Flood Risk Reduction Reservoir System (Plot Site C) will be established, reconnecting the floodplain and enhancing biodiversity, while at the same time leading to a transition of land use by introducing floodplain farming
Potential impacts/benefits:
- floodway used for drought risk reduction, preventing drying of habitats
- floodplain restoration / reconnection
- ecological status restoration
- enhancing biodiversity
- wetland reconversion
- enhance recreation potential for eco-tourism
NbS benefits
- Developing climate change adaptation; improving risk management and resilience
- Flood peak reduction
- Reduce drought risk
- Reduce flood risk
- Reduce run-off
- Carbon sequestration and storage
- Restoring ecosystems and their functions
- Improve connectivity and functionality of green and blue infrastructures
- Increase achievements of biodiversity targets
- Improve water quality
- Increase awareness of NBS solution & their effectiveness and co benefits
- Increase communities’ sense of ownership
- Increase stakeholder awareness & knowledge about NBS
Further information
Sustainable Development Goals
- 1. No Poverty
- 6. Clean Water and Sanitation
- 7. Affordable and Clean Energy
- 8. Decent Work and Economic Growth
- 12. Responsible Consumption and Production
- 13. Climate Action
- 14. Life Below Water
- 15. Life On Land
