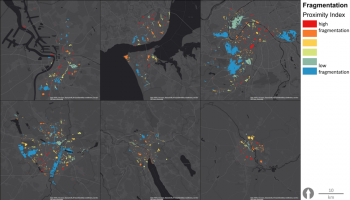
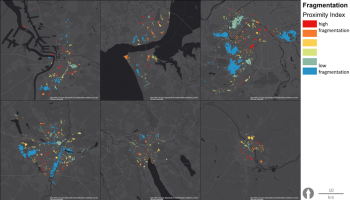
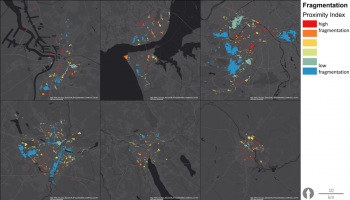
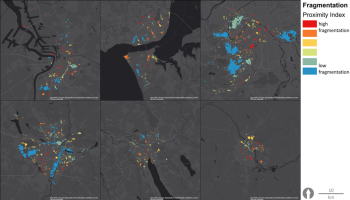
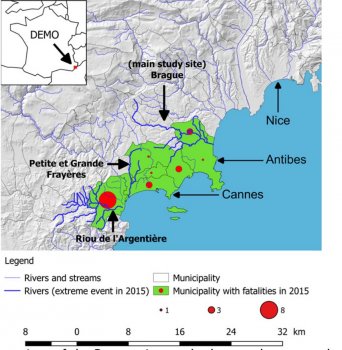
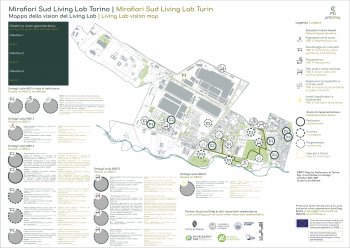
The city’s green and blue areas have a long history, and are even today seen as an important and integrated part of the city of Malmö, as reflected in the recent Master Plan. The ambitions are to create a close, dense, green and mixed functioning city, with densification as a driver, rather than expansion into the outside highly productive farmland. Urban green is a vital component of the future of the city and, in the master plan, is brought forward under such diverse headings as Green City, Green and Blue Environments, Biodiversity, Countryside and Agriculture, Children’s Perspectives,...